Paleontology and Paleoenvironment
Until approximately 201 million years ago, during the Triassic period, the continents were joined together in a single supercontinent known as Pangaea. However, by the end of this geological period, tectonic plate movements caused the breakup of this continent, initiating the opening of the Atlantic Ocean and leading to the separation of the continents we know today.
This separation is associated with an episode of intense volcanism that gave rise to volcanic deposits now found in Europe, Africa, and the Americas, known as the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province (CAMP). In the Alamo Valley, numerous deposits associated with this episode of volcanism can be found, overlain by the geological units corresponding to the last environments that existed in Pangaea before its breakup.
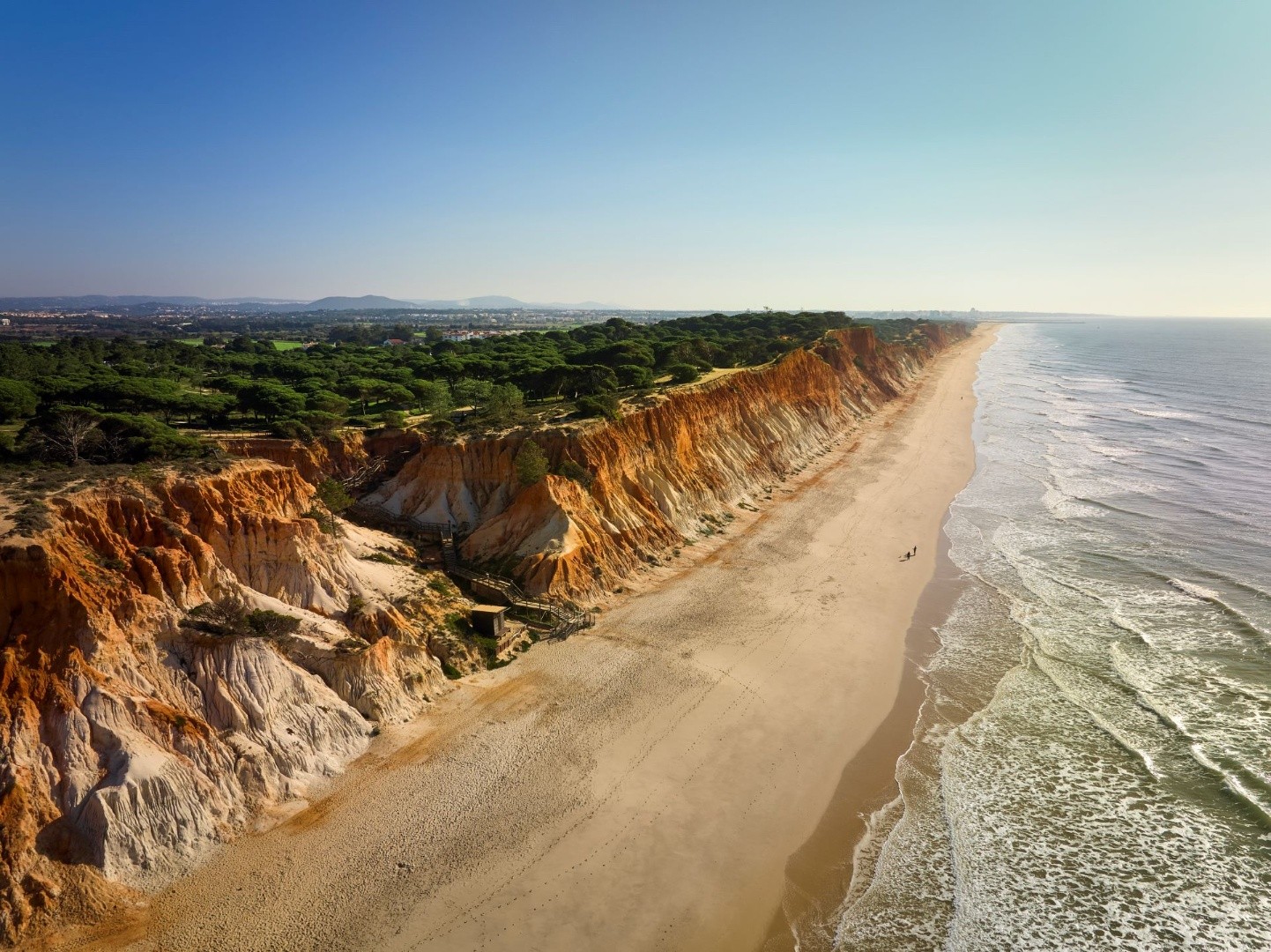
The Alamo Valley is thus an important site for understanding the final phase of Pangaea, its separation, the beginning of the Atlantic's opening, and the associated volcanism.
Locality: